Dr. Paula Goel, Pediatrician & Adolescent Physician
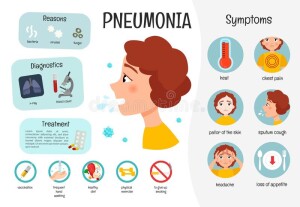
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs in which the air sacs in the lungs (called alveoli) fill up with pus and other fluid. This makes it hard for oxygen to reach the bloodstream. This can occur at any age but is more frightening in children as it may progress rapidly to respiratory distress or failure if not diagnosed and treated in time.
Symptoms vary depending on the age and what caused pneumonia, but can include:
- very fast breathing (in some cases, this is the only symptom)
- breathing with grunting or wheezing sounds
- working hard to breathe; this can include flaring of the nostrils, belly breathing, or movement of the muscles between the ribs
- fever with or without chills
- cough
- stuffy nose
- vomiting
- chest pain
- belly pain (because a child is coughing and working hard to breathe)
- decreased activity or lethargy
- loss of appetite (in older kids) or poor feeding (in infants), which may lead to dehydration
- in extreme cases, bluish or gray color of the lips and fingernails
Pneumonia is caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Mostly caused by viruses. Pneumonia may begin after an upper respiratory tract infection (an infection of the nose and throat), with symptoms starting after 2 or 3 days of a cold or sore throat, after which it progresses to the lungs. Fluid, white blood cells, and debris start to gather in the air spaces of the lungs and block the smooth flow of air to the lungs making it difficult to breathe. If pneumonia is caused by bacteria become sick rapidly starting with a sudden high fever and rapid breathing.
Kids with pneumonia caused by viruses probably will have symptoms that appear more gradually and are less severe, though wheezing can be more common.
Some symptoms give important clues about which germ is causing pneumonia. For example:
- In older kids and teens, pneumonia due to Mycoplasma causes a sore throat, headache, and rash in addition to the usual symptoms of pneumonia.
- In babies, pneumonia due to Chlamydia may cause conjunctivitis (watering red eye)with only mild illness and no fever.
- When pneumonia is due to whooping cough (pertussis), have long coughing spells, turn blue from lack of air, or make the classic “whoop” sound when trying to take a breath.
Diagnosis of pneumonia is made after a medical exam, child’s appearance, breathing pattern, and vital signs, and listen to the lungs for abnormal sounds. Chest X-ray and blood tests may be required.
Viral pneumonia does not require antibiotics for treatment. Pneumonia caused by bacteria is treated with antibiotics taken by mouth at home.
Children might need treatment in a hospital if pneumonia causes a lasting high fever, breathing problems, or if they:
- need oxygen therapy
- have a lung infection that may have spread to the bloodstream
- have a chronic illness that affects the immune system
- are vomiting so much that they cannot take medicine by mouth
- keep getting pneumonia
- might have whooping cough
If your child has bacterial pneumonia and the doctor prescribed antibiotics, give the medicine on schedule for as long as directed. This will help your child recover faster and help prevent the infection from spreading to others in the family. For wheezing, the doctor might recommend using a nebulizer or an inhaler.
The child’s temperature must be taken at least once each morning and each evening. Call the doctor if it goes above 102°F (38.9°C) in an older infant or child, or above 100.4°F (38°C) in a baby under 6 months old.
Check your child’s lips and fingernails to make sure they are rosy and pink. Call your doctor if they are bluish or gray, or the child is breathing very rapidly, which is a sign that the lungs are not getting enough oxygen.
With treatment, most types of bacterial pneumonia are cured in 1–2 weeks. Viral pneumonia may take 4–6 weeks to go away completely.
Can Pneumonia Be Prevented?
Some types of pneumonia can be prevented by vaccines. Kids usually get routine immunizations against Haemophilus influenza, pneumococcus, and whooping cough beginning at 2 months of age.
The flu vaccine is recommended for all healthy kids ages 6 months through 19 years, but especially for kids with chronic illnesses such as heart or lung disorders or asthma.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
You should contact your doctor right away if your child has any of the signs of pneumonia, but especially if he or she:
- has trouble breathing or is breathing too fast
- has a bluish or gray color to the fingernails or lips
- has a fever of 102°F (38.9°C), or above 100.4°F (38°C) in babies younger than 6 months old